Radiative decays
Property of the radiative decays Kl2γ (K+→ l+νγ)
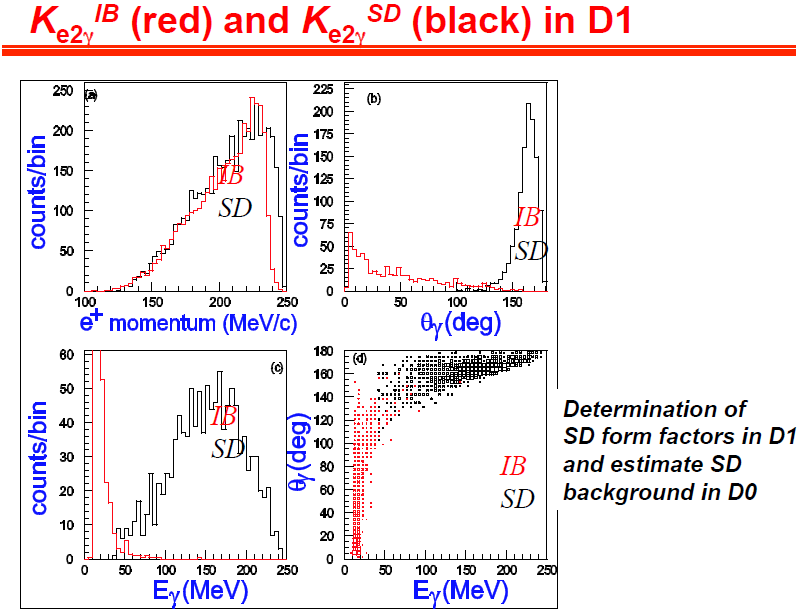
In order to compare the experimental RK value with the SM prediction, the internal bremsstrahlung process in radiative K+ → e+ ν γ (KIB e2γ) and K+ → μ +ν γ (KIB μ 2 γ) decays has to be included into the Ke2 and Kμ2 samples, respectively. On the other hand, the Structure Dependent (SD) events are backgrounds for the present experiment and have to be subtracted from the observed sample.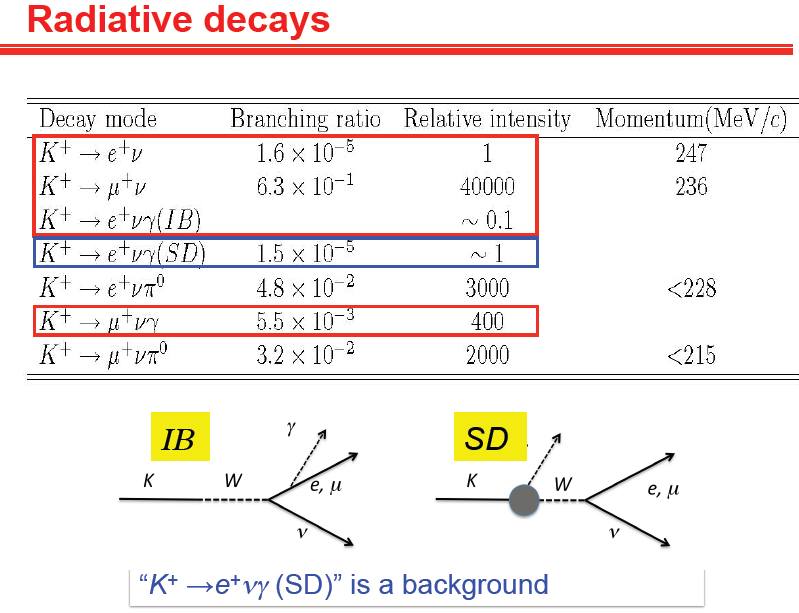
Characteristics of the radiative decays
According to the Monte Carlo simulation, K+ → e+ν with a external bremsstrahlung photon is not detected by the calorimeter. Also, most of the radiative IB photons pass though the muon hole, while a part of Kl2γ events can be detected by the calorimeter. For the determination of RK, the radiative corrected Ke2+KIB e2 γ and Kμ2 + KIB μ2 γ events have to be analyzed. On the other hand, the SD events are backgrounds for the present experiment and have to be subtracted from the observed sample. For this purpose, the reproducibility of the observed IB and SD spectra by a Monte Carlo simulation is very important for the understanding of these physics processes.