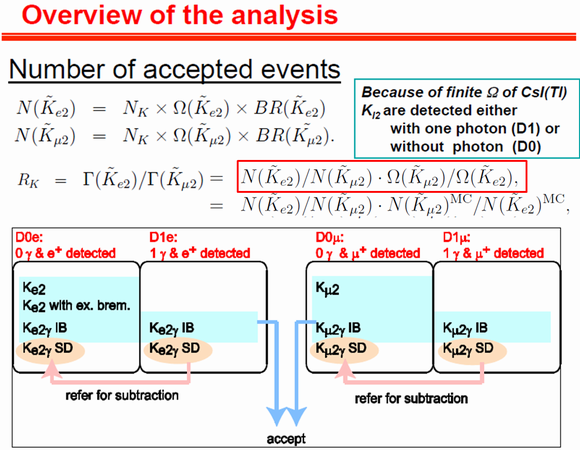
Overview of the analysis
Ke2 (K+→ e+ν) / Kμ2(K+→ μ+ν) separation
In order to remove Ke3 and Kμ3 backgrounds, Ke2 and Kμ2 events are identified by requiring the e+ and μ+ momentum to be higher than the Ke3 and Kμ3 endpoints as shown in the figure. Particle discrimination between e+ and μ+ is carried out using an aerogel Cherenkov counters (AC) and a lead-glass Cherenkov counter (PGC), and by measuring the time-of-flight (TOF) between the TOF1 and TOF2 scintillation counters.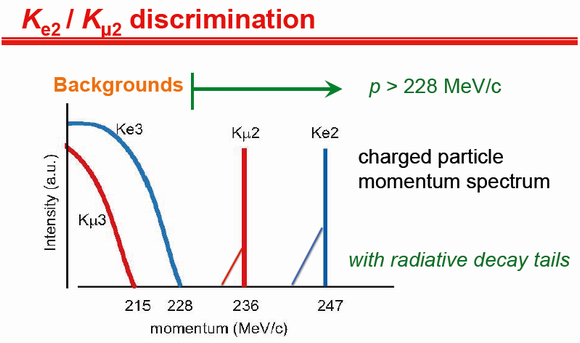
Separation of Ke2/Kμ2
- e/μ separation not only in momentum spectrum but with PID using TOF+AC + PGC
- Inclusion of radiative decay (CsI(Tl))
- Rejection of Ke3 and Kμ3
Overview of the analysis
The number of accepted Ke2 and Kμ2 events,, after background subtraction can be described as,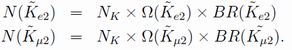
Here NK is the number of stopped kaon in the target, BR is the branching ratio, and Ω is the acceptance. Therefore, the RK = Γ(Ke2)/ Γ(Kμ2) ratio can be obtained by making the ratio of the accepted Ke2 to Kμ2 event numbers corrected for the detector acceptance as,
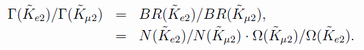
The detector acceptance is calculated by Monte Carlo simulation. It is to be noted that the analysis procedure is exactly identical between Ke2 and Kμ2 except for the particle identification in order to reduce the systematic error due to the analysis.